Is Cytoskeleton In Plant And Animal Cells
The nucleus and cellular organelles are not randomly scattered in the cytoplasm. Indeed, there is a functional and structural internal system ruled by several types of proteins arranged in filaments, jointly known every bit cytoskeleton. These filaments class a dynamic scaffolding distributed through the cytosol, although some of them are constitute inside the nucleus.
The give-and-take "cytoskeleton" is a morphological and structural term coming from the early observations of cells at electron microscopy. Information technology may lead to a misunderstanding because the cytoskeleton is non a static scaffold for supporting jail cell structures. Actually, information technology is a very plastic construction responsible for cell movement and shape, and for organelle system and movements. The functional variety of the cytoskeleton is a issue of its molecular features.
P olymerization and depolymerization. Cytoskeleton filaments are formed by polymerization of repeated proteins that do not constitute chemic bonds betwixt each other, but they are linked through electrical forces. In this way, filaments can be assembled (polymerized) and disassembled (depolymerized) easily and according to the cell needs. Cell may grade and modify filament scaffolds where they are needed. Proteins that forms cytoskeleton filaments are always changing between polymerized and free in the cytosol.
P olarization. Some cytoskeletal filaments are polarized structures, that is, all the protein units in the filament are in the aforementioned orientation. Thus, the ii ends of the filament are dissimilar. This organisation is important for filament growing and for those proteins that move along the filament.
R egulation. Cells have many proteins to command the organization and activity of cytoskeleton filaments. They are tools for manipulating the three dimensional scaffold of cytoskeleton filaments. For instance, motor proteins are molecules that employ cytoskeletal filaments as train rails to transport cargoes (vesicles, organelles, macromolecules) through the cytoplasm. Other proteins are involved in filament polymerization-depolymerization, filament stability, or are intermediaries between filaments and other jail cell structures.
Cytoskeleton performs an amazing amount of functions in eukaryotic cells. Information technology makes cells to movement, establishes the jail cell shape, makes possible the polarity of some cells, distributes intracellular organelles properly, is responsible for the communication between those organelles, and for exocytosis and endocytosis processes, runs jail cell division (both mitosis and meiosis), is a good scaffold for maintaining intracellular organization, resists mechanical forces, withstands jail cell deformations, and many others. Although some homologous cytoskeletal proteins have been constitute in prokaryotes, cytoskeleton appears to be invented past eukaryotic cells. The mechanical function of cytoskeleton is particularly useful in animal cells, where no cell wall gives consistency to the cell. Without a cytoskeleton, animal cells will break because plasma membrane is only a sheet of fat.
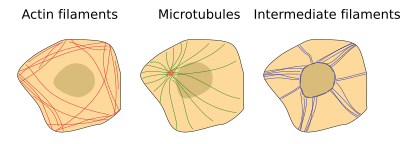
Cytoskeleton is equanimous of three types of filaments: actin filaments or microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments (Effigy ane). Actin filaments, polymers of repeated units of the actin protein, are in charge of cell movements, endocytosis, phagocytosis, cytokinesis, and other functions. They are as well function of the molecular machinery needed for muscle contraction, and contribute to form some cell junctions (adherent junctions and tight junctions). They are named as microfilaments because their diameter is lower than those of the other cytoskeleton components. Microtubules, as the name suggests, are tubules made up of dimers of α- and β-tubulin. Microtubules are needed for the intracellular motion of organelles and vesicles, constitute the skeleton of cilia and flagella, bulldoze the chromosome segregation during cell partitioning, etcetera. Actin filaments and microtubules are helped by motor proteins, which are bodily motors that can move along the filaments. Actin filaments and microtubules are used as rail by motor proteins to conduct cargoes. Cargoes may be chromosomes, organelles, or macromolecular complexes. Intermediate filaments are responsible for cell integrity, since they office as potent intracellular cables anchored to cell junctions similar desmosomes and hemidesmosomes. They make possible the adhesion between contiguous cells and cell-extracellular matrix, contributing to the cohesion of tissues. They are specialized in withstanding mechanical forces. Unlike the other components of the cytoskeleton, intermediate filaments are polymers that tin can exist made up of different families of proteins, such equally keratins, vimentins, laminas, and some others.
Source: https://mmegias.webs.uvigo.es/02-english/5-celulas/7-citoesqueleto.php
Posted by: oliveirahileboseek.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is Cytoskeleton In Plant And Animal Cells"
Post a Comment